Types of Aortic Aneurysm
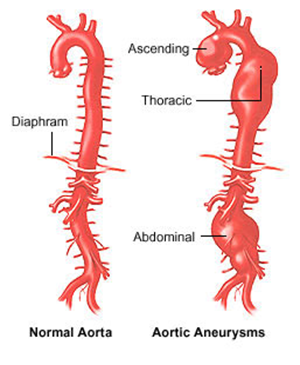
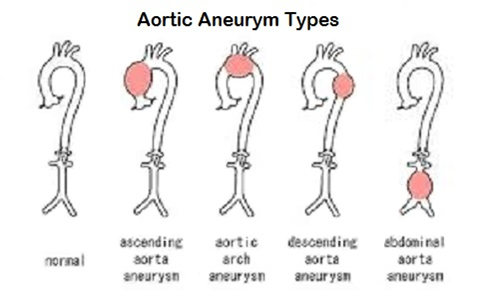
 Image Removed
Image Removed
Renal Artery Aneurysm
 Image Added
Image Added
Often times when patients complain about chest discomforts and pain, the occurrence of aneurysm(s) are suspected. It is difficult to pinpoint the exact location of the aneurysm. Hence MRI and CT scan are the most frequently used tools to detect the presence and location of aneurysms. In this scenario, the test locations are often broadly defined as the subject's chest, abdominal cavity or the whole body. The specific location(s) where aneurysms are identified/found should be mapped to result location, not testThis example shows a discrete aneurysm in the aorta. In this instance, the MRI imagining identified the presence of an aneurysm in the chest of a subject, which is in the aorta (RESLOC), extending from the aortic arch to the abdominal aorta (RLOCTX).
| Dataset wrap |
|---|
|
| Rowcaps |
|---|
Rows 1-2: | Show the presence of subject ABC-123 has a single aortic aneurysm from a chest CT scan. |
|---|
Rows Row 3-4: | Show the Shows the said aneurysm is 7.5cm in length (diameter), which is measured from the aortic arch to the abdominal aorta and 3.7cm in widthAortic Arch to Descending Aorta |
|---|
| Rows 4-5: | Show subject ABC-456 is found to have aneurysms in two locations from a whole-body MRI Scan: RENAL ARTERY and THORACIC AORTA. |
|---|
|
| Dataset2 |
|---|
Row | STUDYID | DOMAIN | USUBJID | CVSEQ | CVGRPID | CVTEST | CVORRES | CVORRESU |
|---|
CVLOCCVTSTLOC | CVMETHOD | VISITNUM | VISIT | CVDTC |
|---|
CVRESLOC 1CVRESLOC 1CVRLOCTX | | 1 | ABC | CV | ABC-123 | 1 | 1 | Aneurysm Indicator | Y |
|---|
MRI| CT SCAN | 1 | BASELINE | 2020-04-27 |
| |
|
| | 2 | ABC | CV | ABC-123 | 2 | 1 | Number of Aneurysms | 1 |
|---|
| MRI| CT SCAN | 1 | BASELINE | 2020-04-27 |
| |
|
| | 3 | ABC | CV | ABC-123 | 3 | 1 | Aneurysm Length/Diameter | 7.5 | CM | CHEST |
|---|
MRI| CT SCAN | 1 | BASELINE | 2020-04-27 |
Abdominal Aorta| Descending Aorta | | 4 | ABC | CV | ABC-456 | 1 | 2 | Aneurysm Indicator | Y |
|---|
ABDOMINAL CAVITY
| BODY | MRI | 1 | BASELINE | 2020-04-27 |
| RENAL ARTERY | THORACIC AORTA |
| | 5 | ABC | CV | ABC-456 | 2 | 2 | Number of Aneurysms | 2 |
|---|
ABDOMINAL CAVITY
| BODY | MRI | 1 | BASELINE | 2020-04-27 |
| RENAL ARTERY |
ABDOMINAL AORTA | |
|
From the CV-imaging project we also encountered use-cases where we need sub-LOC variables to help to further specify the free-text, detailed, more granular locations where a test is performed. These values are indeed clinically relevant location information that should NOT be pre-coordinated into the TEST itself, but are also inappropriate for LOC.
So we need a variable that provides additional, more specific and granular information about a proximate location or a range of location(s).

This example shows the minor axis cross-sectional diameter measurements of the left and right ventricle of the heart, at end ventricular diastole.
| Dataset wrap |
|---|
|
| Rowcaps |
|---|
Row 1: | Shows the cross-sectional diameter of the left ventricle at end ventricular diastole, measured along the minor axis and specifically at the location of the high papillary muscle. The further anatomical details more granular, free-text anatomical description at which the measurement is set and performed is represented by the CVLOCTX CVTLODTL NSV. |
|---|
Row 2: | Shows the cross-sectional diameter of the right ventricle at end ventricular diastole, measured along the minor axis and specifically at just below the tricuspid valve. The further anatomical details more granular, free-text anatomical description at which the measurement is set and performed is represented by the CVLOCTX CVTLODTL NSV. |
|---|
|
| Dataset2 |
|---|
Row | STUDYID | DOMAIN | USUBJID | CVSEQ | CVTESTCD | CVTEST | CVORRES | CVORRESU |
|---|
CVLOCCVTSTLOC | CVMETHOD | VISITNUM | VISIT | CVDTC |
|---|
CVLOCTX | | 1 | ABC | CV | ABC-123 | 1 | MNDIAEVD | Minor Axis Cross-sec Diameter, EVD | 3.7 | CM | HEART, LEFT VENTRICLE | TTE | 1 | BASELINE |
|---|
| | High
|
| At high papillary muscle level | | 2 | ABC | CV | ABC-123 | 2 | MNDIAEVD | Minor Axis Cross-sec Diameter, EVD | 3.2 | Cm | HEART, RIGHT VENTRICLE | TTE | 1 | BASELINE |
|---|
| |
|
| Below the tricuspid valve |
|
|
...




