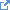
| Element Name | TranslatedText |
|---|---|
| Parent Elements | Decode, ErrorMessage, Question, Description, Annotation |
| Element Textual Value | text |
| Usage |
|
| Attributes | xml:lang, type |
| Child Elements | None |
| Attribute | Usage | Allowable Values | Description | Business Rule(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
xml:lang | Optional | See IETF Trust, Tags for Identifying Languages (Section 2.2, References) Samples:
| Code representing the language of the enclosed text value. Default value depends on locale. Note: The xml:lang attribute is part of the XML standard. |
|
| type | Required | text/plain, application/xhtml+xml | Contains IANA media type of the TranslatedText element contents. Default value: "text/plain". |
|
Description
Human-readable text that is appropriate for a particular language. TranslatedText elements typically occur in a series, presenting a set of alternative textual renditions for different languages and types.
To find the text appropriate for a target language with tag LT, search for a TranslatedText element whose xml:lang attribute matches LT exactly (ignoring case). If that fails, remove the ending subtag from LT and repeat. If that fails, search for a TranslatedText without an xml:lang attribute and use that. If none is found, there is no suitable text available. E.g.
| TranslatedTexts Present | Requested | Process |
| <TranslatedText xml:lang="fr-CA">... <TranslatedText xml:lang="en-GB">... <TranslatedText>... | fr-FR | Look for xml:lang="fr-FR". This is not found, so look for xml:lang="fr". This is not found, so look for a TranslatedText with no xml:lang. This is the text that should be used. |
XHTML
For type="application/xhtml+xml" it is possible to use HTML tags for text formatting. Value of the TranslatedText element must be always wrapped in <div> tag with non-whitespace content within it. The <div> must have a proper namespace specified: <div xmlns="https://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml/>
Note that the XHTML is contained in general XML so there is no support for HTML entities like or © etc. Unicode characters shall be used instead. Unicode   substitutes for .
The content should be in the language of the TranslatedText element (xml:lang), but there is no reason to expect that HTML type tooling would understand the TranslatedText element language. For this reason, it is a good practice to use a lang attribute on the <div> (see the note in the HTML 5 specification about use of language ).
A minimum set of supported HTML tags
A base minimum set of HTML tags which needs to be supported for ODM conformance:
- Layout: <div> <p> <br>
- Headers: <h1> <h2> <h3> <h4> <h5> <h6>
- Text styling: <strong> <em> <sup> <sub>
- Quotes/Unformatted/Code: <blockquote> <code> <pre>
- Lists: <ul> <ol> <li>
- Tables: <table> <thead> <tbody> <tr> <th> <td>
- Lines: <hr>
- Links: <a>
- Images: <img>
- Color: <span style="color:xxx">
Examples
Method description with XHTML formatting.
<Description>
<TranslatedText xml:lang="en" type="text/plain">Study Day Derivation
Study day (ADY) is derived differently for events occurring:
Before the first dose date.
On or after the first dose date.
When the event date (ADT) is before the first dose date (TRTSDT):
ADY = ADT - TRTSTDT.
When the event date (ADT) is on or after the first dose date (TRTSDT):
ADY = ADT - TRTSTDT + 1.
</TranslatedText>
<TranslatedText xml:lang="en" type="application/xhtml+xml">
<div xmlns="https://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml/">
<h3>Study Day Derivation</h3>
<p><strong>Study day</strong> (ADY) is derived differently for events occurring:</p>
<ol>
<li>Before the first dose date.</li>
<li>On or after the first dose date.</li>
</ol>
<p>When the event date (<em>ADT</em>) is before the first dose date (<em>TRTSDT</em>):</p>
<p><code>ADY = ADT - TRTSTDT.</code></p>
<p>When the event date (<em>ADT</em>) is on or after the first dose date (<em>TRTSDT</em>):</p>
<p><code>ADY = ADT - TRTSTDT + 1.</code></p>
</div>
</TranslatedText>
</Description>