- Created by Lou Ann Kramer, last modified on Feb 03, 2023
You are viewing an old version of this page. View the current version.
Compare with Current View Page History
« Previous Version 90 Next »
This is an example showing trial design and results data of Study #123 for the determination of the in vitro genotoxicity potential of 10 tobacco products in the in vitro Micronucleus Assay
For the purposes of team review of the example data, the report is included in this section:
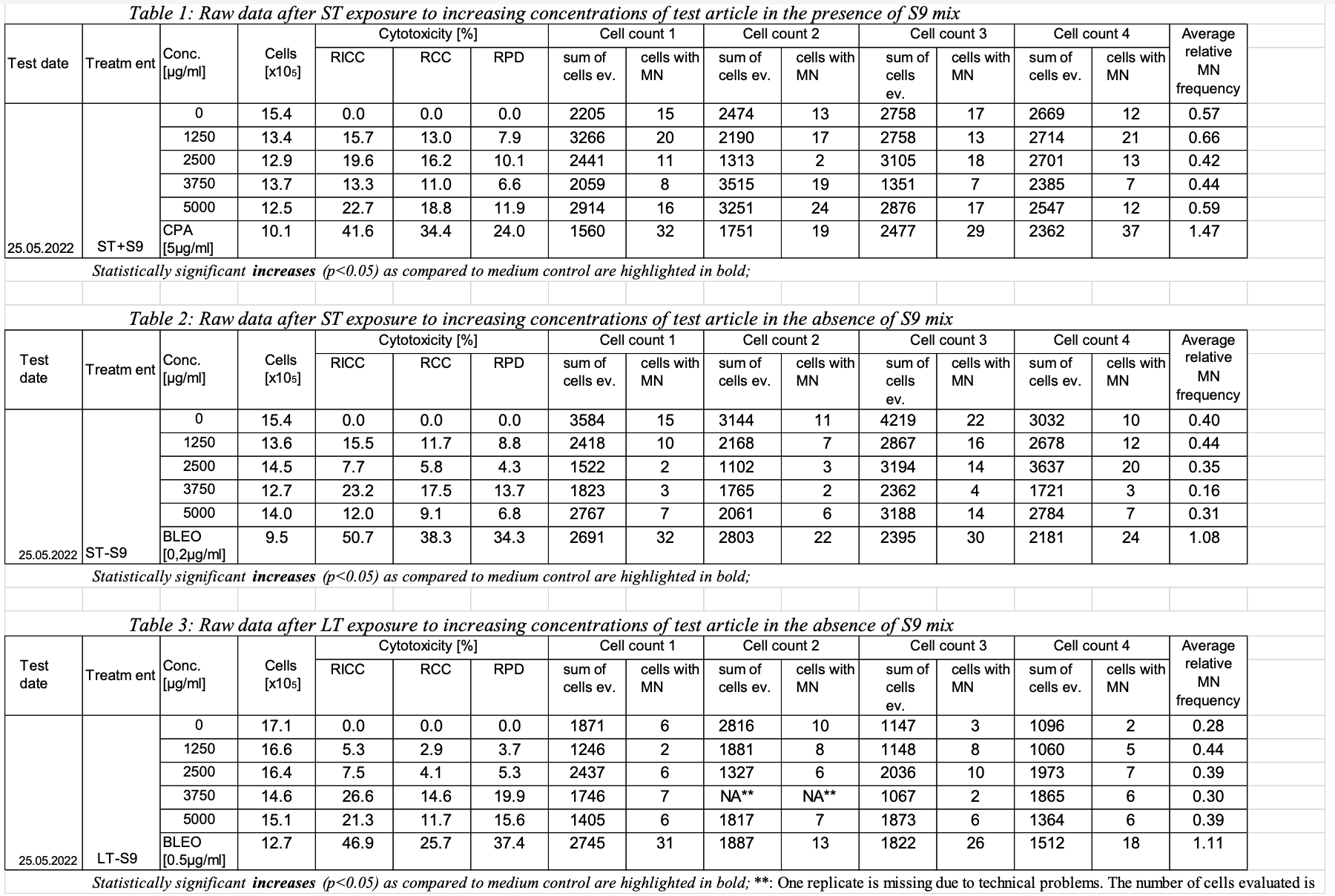
Sample data #1: Determination of the in vitro genotoxicity potential of 10 tobacco products in the in vitro Micronucleus Assay
Study info: This study was performed to assess the in vitro genotoxicity of 10 different tobacco products containing 1% to 2% nicotine. The genotoxic potential was determined using the in vitro micronucleus test with TK6 lymphoblastoid suspension cells. The study was conducted in compliance with the following documents:
- OECD TG 487 (2010): Guideline for the testing of chemicals: In vitro mammalian cell micronucleus test.
- BL SOP 132: Determination of the in vitro genotoxicity of condensates from tobacco products and ingredients for tobacco products / electronic vapour products – in vitro micronucleus test (IVM) with TK6 cells.
The cells were exposed to increasing dose levels of tobacco product using short term treatment in the presence and absence of an external metabolic activation system (ST+/-S9 mix) as well as a long term treatment in the absence of an external metabolic activation system (LT-S9 mix).
Toxicity was calculated as relative increase in cell count (RICC), relative cell count (RCC) and relative population doubling (RPD). RPD is the cytotoxicity measure used for the assessment. RICC and RCC are also reported but not considered for the assessment.
Note: OECD GUIDELINE FOR THE TESTING OF CHEMICALS
Population Doubling = [log (Post-treatment cell number ÷ Initial cell number)] ÷ log 2
Conclusion: All tobacco product evaluated did not induce any signs of severe toxicity or genotoxicity in any of the treatments and do not fulfil the criteria to be classified as genotoxic.
Reported results: (only listed the result of one tobacco product as an example)
- Statistical analysis
Adjusted p-values calculated for the micronucleus frequencies for every dose level as compared to the corresponding solvent control after ST in the presence and absence of S9 mix as well as LT in the absence of S9 mix. One way ANOVA with posthoc Dunnett’s test for multiple comparisons for the dose response and a two tailed unpaired student’s t-test for the comparison of positive and negative control were used. The difference between the samples is considered statistically significant at p≤0.05.
Treatment | Test date | Concentration [µg/ml] | Fold increase of MN over background | Adjusted p- value | Significant increase Y/N |
ST+ S9 | 25.05.2022 | 1250 | 0.9 | 0.9973 | N |
2500 | 0.9 | 0.9517 | N | ||
3750 | 0.6 | 0.2654 | N | ||
5000 | 0.9 | 0.9895 | N | ||
CPA [5µg/ml] | 3.1 | 0.0003 | Y | ||
ST-S9 | 25.05.2022 | 1250 | 1.6 | 0.6408 | N |
2500 | 1.3 | 0.8995 | N | ||
3750 | 2.9 | 0.0106 | N | ||
5000 | 1.0 | > 0.9999 | N | ||
Bleo [0.2µg/ml] | 3.8 | 0.0002 | Y | ||
LT-S9 | 25.05.2022 | 1250 | 0.7 | 0.5958 | N |
2500 | 1.3 | 0.6378 | N | ||
3750 | 0.5 | 0.1146 | N | ||
5000 | 1.1 | 0.9929 | N | ||
Bleo [0.5µg/ml] | 2.9 | 0.0047 | Y |
Bleo: Bleomycin; CPA: Cyclophosphamid A; statistically significant increases are highlighted in bold.
- Assumption: The intent of this dataset is to provide a summary of trial (study) information. This is not subject-level data.
- Assumption: A Trial (study) can have more than one assay type
- Assumption: ASSAYID value of ALL indicates that it applies to all assays in the study
- Assumption: SPDEVID and DUREFID should only be in TX (with the same value for all sets if there is only one device used)
- Assumption: SPDEVID (sponsor defined device identifier) should be added at the trial set level (tx.xpt) - we can discuss if this should be in TS when there is only one device for a study
- This allows for studies where there are multiple products and different product(s) per trial set, one record for each product that is being tested in each particular trial set (tx.xpt)
Row | STUDYID | ASSAYID | DOMAIN | TSSEQ | TSGRPID | TSPARMCD | TSPARM | TSVAL | TSVALNF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | GLPTYP | Good Laboratory Practice Type | FDA | ||
| 2 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 2 | GLPTYP | Good Laboratory Practice Type | OECD | ||
| 3 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | STSTDTC | Study Start Date | 2022-05-25 | ||
| 4 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | STITLE | Study Title | Determination of the in vitro genotoxicity potential of 10 tobacco products in the in vitro Micronucleus Assay | ||
| 5 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | SNDIGVER | SEND Implementation Guide Version | TOBACCO IMPLEMENTATION GUIDE VERSION 1.0 | ||
| 6 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | SNDCTVER | SEND Controlled Terminology Version | SEND Terminology 2021-09-30 | ||
| 7 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | SSPONSOR | Sponsor Organization | Example Sponsor Inc. | ||
| 8 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | SPREFID | Sponsor's Study Reference ID | NOT APPLICABLE | ||
| 9 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | 1 | TSTFNAM | Test Facility Name | Example Tox Lab Name | |
| 10 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | 1 | TSTFLOC | Test Facility Location | 10 Somewhere Street, Montgomery, AL 10000 | |
| 11 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | 1 | TFCNTRY | Test Facility Country | USA | |
| 12 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | 1 | STDIR | Study Director | Dr. R. Smith | |
| 13 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | GLPFL | GLP Flag | Y | ||
| 14 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | ASTD | Assay Standard | OECD Test No. 487 | ||
| 15 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | ASTDV | Assay Standard Version | 2016-07-29 | ||
| 16 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | SSTYP | Study Type | GENOTOXICITY IN VITRO | ||
| 17 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | SSSTYP | Study Sub Type | In Vitro Micronucleus | ||
| 18 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | SPECIES | Species | Homo Sapiens | ||
| 19 | 123 | MNvit | TS | 1 | TESTSYS | Test System | TK6 Lymphoblastoid Suspension Cells |
(This is a copy from the SDTM Example. Cigarette Design Parameters, will need scription team)
| Rows 1-4: | Show the records for the product identifiers for the tobacco product identified in SPTOBID. These records are categorized as product identifiers by TOCAT = PRODUCT IDENTIFIERS. |
|---|---|
| Rows 5-10: | Show the records for the product descriptors for the tobacco product identified in SPTOBID. These records are categorized as product identifiers by TOCAT = PRODUCT DESCRIPTOR. |
to.xpt
Row | STUDYID | DOMAIN | SPTOBID | TOSEQ | TOTESTCD | TOTEST | TOCAT | TOORRES | TOORRESU | TOSTRESC | TOSTRESN | TOSTRESU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TOB07 | TO | CIG01a | 1 | TBPRDCAT | Tobacco Product Category | PRODUCT IDENTIFIER | Cigarette | Cigarette | |||
| 2 | TOB07 | TO | CIG01a | 2 | TBPRSCAT | Tobacco Product Subcategory | PRODUCT IDENTIFIER | Filtered, Combusted | Filtered, Combusted | |||
| 3 | TOB07 | TO | CIG01a | 3 | MANUF | Manufacturer | PRODUCT IDENTIFIER | Joes Cigs USA | Joes Cigs USA | |||
| 4 | TOB07 | TO | CIG01a | 4 | TRADENAM | Trade Name | PRODUCT IDENTIFIER | Treetop Menthol King Size | Treetop Menthol King Size | |||
| 5 | TOB07 | TO | CIG01a | 5 | PACKTYP | Package Type | PRODUCT DESCRIPTOR | HARD PACK | HARD PACK | |||
| 6 | TOB07 | TO | CIG01a | 6 | PRDQUAN | Product Quantity | PRODUCT DESCRIPTOR | 20 | CIGARETTE | 20 | 20 | CIGARETTE |
| 7 | TOB07 | TO | CIG01a | 7 | LENGTH | Length | PRODUCT DESCRIPTOR | 86.0 | mm | 86.0 | 86.0 | mm |
| 8 | TOB07 | TO | CIG01a | 8 | CIRCUMF | Circumference | PRODUCT DESCRIPTOR | 26.0 | mm | 26.0 | 26.0 | mm |
| 9 | TOB07 | TO | CIG01a | 9 | VENTLTN | Ventilation | PRODUCT DESCRIPTOR | 10.0 | % | 10.0 | 10.0 | % |
| 10 | TOB07 | TO | CIG01a | 10 | CHARFLAV | Characterizing Flavor | PRODUCT DESCRIPTOR | MENTHOL | MENTHOL |
- During CT definition/reviews will decide appropriate TXPARM and TXVAL; Treatment duration may be controlled; For now, we just include good example values based on our experience
- Assumption: The Trial Sets (TX) domain provides the list of distinct sets of subjects having different experimental factors, treatment factors, inherent characteristics, or distinct sponsor designations as specified in the trial design.
- Where is TK6 cell type? is this test system (see below)
- needs to be allowed to vary down to the well level / result level
- Do we need both SPDEVID AND DUREFID?
- What are good values (realistic) for "SET"?
- Check Essential Data list
A1: 
A2: 
| Row | STUDYID | ASSAYID | DOMAIN | SETCD | SET (what sponsor calls it, more meaningful label for Tables) | TXSEQ | TXPARMCD | TXPARM | TXVAL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 (table 1, row 1, ST exposure with S9) | ST+S9C0 | 1 | METACT | Metabolic Activation (this is the type of activation used) | +S9 |
| 2 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 2 | METACTFL | Y/N presence of metabolic activation (this indicates that metabolic activation was used) | Y |
| 3 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 3 | TRTDMIN | Treatment Duration Minimum | 3 |
| 4 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 4 | TRTDTRG | Treatment Duration Target | 3.5 |
| 5 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 5 | TRTDMAX | Treatment Duration Maximum | 4 |
| 6 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 6 | TRTDU | Treatment Duration Unit | HOURS |
| 7 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 7 | RCVDMIN | Recovery Duration Minimum | 23.5 |
| 8 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 8 | RCVDTRG | Recovery Duration Target | 24 |
| 9 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 9 | RCVDMAX | Recovery Duration Maximum | 24.5 |
| 10 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 10 | RCVDU | Recovery Duration Unit | HOURS |
| 11 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 11 | INCBTMP | Incubation Temperature | 37 |
| 12 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 12 | INCBTMPU | Incubation Temperature Unit | C |
| 14 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 14 | HUMID | Atmospheric Relative Humidity Percent | 50 |
| 15 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 15 | ATMCO2 | Atmospheric CO2 Percent | 5 |
| 16 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 16 | SPTOBID | Sponsor defined tobacco identifier | CIG01a |
| 17 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 17 | EXPTYP | Exposure Type (See TIG NC workstream minutes 30-Jan here: Nonclinical) | Submerged |
| 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 18 | SAMTYP | Sample Type (e.g. TPM, GVP, whole aerosol, whole smoke conditioned media, aqueous extracts, etc., see notes here: Nonclinical) | Total Particulate Matter in DMSO | |
| 18 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 6 | INTRVN | Name of the Intervention Article can be: Tobacco ProdA, Bleomycin (positive control) or Cyclophosphamid A (positive control) | Tobacco ProdA |
| 19 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 7 | ITVTYPE | type of intervention article choices of values: product; negative control; positive control | Negative Control |
| 20 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 8 | ITVCONC | Concentration of intervention article | 0 |
| 21 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 9 | ITVCONCU | Concentration Unit | ug/ml |
| 22 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 10 | SPDEVID | Sponsor defined device identifier | PUFFMASTER3K |
| 23 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A1 | ST+S9C0 | 11 | DUREFID | Smoke Regimen | Medium Intensity Regimen |
| 25 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A2 (table 1, row 2, ST exposure with S9 at concentration 1250) | ST+S9-1250 | 1 | METACT | Metabolic Activation (should there be two parms? Presence, type)? | +S9 |
| 26 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A2 | ST+S9-1250 | 2 | METACTFL | Y/N presence of metabolic activation (this indicates that metabolic activation was used) | Y |
| 27 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A2 | ST+S9-1250 | 3 | TRTDRTRG | Treatment Duration target. (how do we show 3-6 hour range? start/end, target and tolerance?, one text field not-analyzable) | 3 |
| 28 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A2 | ST+S9-1250 | 4 | TRTDRTOL | Treatment Duration Tolerance | |
| 29 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A2 | ST+S9-1250 | 5 | TRTDURU | Treatment Duration Unit (this is for both TRTDURT, TRTDURTOL) | H |
| 30 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A2 | ST+S9-1250 | 6 | INTRVN | name of the intervention article | Tobacco ProdA |
| 31 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A2 | ST+S9-1250 | 7 | ITVTYPE | type of intervention article | Product |
| 32 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A2 | ST+S9-1250 | 8 | ITVCONC | Concentration of i a | 1250 |
| 33 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A2 | ST+S9-1250 | 9 | ITVCONCU | Concentration Unit | ug/ml |
| 34 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A2 | ST+S9-1250 | 10 | SPDEVID | Sponsor defined device identifier | PUFFMASTER2023 |
| 35 | 123 | MNvit | TX | A2 | ST+S9-1250 | 11 | DUREFID | Smoke Regimen | High Intensity Regimen |
| ... |
We use DU for smoking regimen. Note that a separate DI dataset will be needed to show identifying parameters of the "PUFFMASTER3K" smoking machine
- Details of the smoking regimen are represented as device in-use properties, linked to the stability data in PT above by matching values of PTREFID/DUREFID = "Medium Intensity Regimen" (We will update with a realistic value for the regimen, with input).
- Smoking regimen is represented in --REFID (we made up a value of "Medium Intensity Regimen"; we can update with something realistic)
- The smoking regimen is carried out by the smoking machine/device shown in SPDEVID, Sponsor defined device identifier, "PUFFMASTER3K"
du.xpt
Row | STUDYID | DOMAIN | SPDEVID | DUSEQ | DUREFID | DUGRPID | DUTESTCD | DUTEST | DUORRES | DUORRESU | DUSTRESC | DUSTRESN | DUSTRESU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER3K | 1 | Medium Intensity Regimen | PUFFPROF | Puff Profile | SQUARE | SQUARE | ||||
| 2 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER3K | 2 | Medium Intensity Regimen | PUFFDUR | Puff Duration | 1.25 | sec | 1.25 | 1.25 | sec | |
| 3 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER3K | 3 | Medium Intensity Regimen | PUFFINT | Puff Interval | 3 | PUFF/min | 3 | 3 | PUFF/min | |
| 4 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER3K | 4 | Medium Intensity Regimen | PUFFBLCK | Puff Block | 25 | % | 25 | 25 | % | |
| 5 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER3K | 5 | Medium Intensity Regimen | NUMPUFF | Total Number of Puffs | 200 | PUFF | 200 | 200 | PUFF | |
| 6 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER3K | 6 | Medium Intensity Regimen | PUFFVOL | Puff Volume | 10 | mL | 10 | 10 | mL | |
| 7 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER3K | 7 | Medium Intensity Regimen | PUFFRNG | Puff Range | 100-200 | 100-200 | ||||
| 8 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER3K | 8 | Medium Intensity Regimen | 1 | PUFFPAUS | Puff Pause | 60 | s | 60 | 60 | s |
| 9 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER3K | 9 | Medium Intensity Regimen | 1 | PUFFPINT | Puff Pause Interval | 10 | PUFF | 10 | 10 | PUFF |
| 10 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER2023 | 1 | Canadian Intense Regime | PUFFPROF | Puff Profile | SQUARE | SQUARE | ||||
| 11 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER2023 | 2 | Canadian Intense Regime | PUFFDUR | Puff Duration | 2.00 | sec | 2.00 | 2.00 | sec | |
| 12 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER2023 | 3 | Canadian Intense Regime | PUFFINT | Puff Interval | 4 | PUFF/min | 4 | 4 | PUFF/min | |
| 13 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER2023 | 4 | Canadian Intense Regime | PUFFBLCK | Puff Block | 0 | % | 0 | 0 | % | |
| 14 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER2023 | 5 | Canadian Intense Regime | NUMPUFF | Total Number of Puffs | 200 | PUFF | 200 | 200 | PUFF | |
| 15 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER2023 | 6 | Canadian Intense Regime | PUFFVOL | Puff Volume | 10 | mL | 10 | 10 | mL | |
| 16 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER2023 | 7 | Canadian Intense Regime | PUFFRNG | Puff Range | 100-200 | 100-200 | ||||
| 17 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER2023 | 8 | Canadian Intense Regime | 1 | PUFFPAUS | Puff Pause | 60 | s | 60 | 60 | s |
| 18 | 123 | DU | PUFFMASTER2023 | 9 | Canadian Intense Regime | 1 | PUFFPINT | Puff Pause Interval | 10 | PUFF | 10 | 10 | PUFF |
di.xpt (copied v1.0 of medical devices IG)
- This example is a copy of Example 1 from di.xpt in SDTMIG-MD v1.0 but with values for SPDEVID and DIVAL revised slightly.
- Should I remove the FDA UDI (row 5) unless CTP has or plans to establish UDI values?
Example 1
This shows records for two three devices where the sponsor felt that the type, manufacturer, model number, and serial number were necessary for unique identification. In addition, there was a post-marketing UDI identifier available for the first device.
- Rows 1-5 show the records for a device given a SPDEVID of PUFFMASTER3K
- Rows 5-8 show the records for a device given a SPDEVID of PUFFMASTER2023
- Rows 9-12 show
Row | STUDYID | DOMAIN | SPDEVID | DISEQ | DIPARMCD | DIPARM | DIVAL |
1 | 123 | DI | PUFFMASTER3K | 1 | DEVTYPE | Device Type | ENDS |
2 | 123 | DI | PUFFMASTER3K | 2 | MANUF | Manufacturer | Acme Machines |
3 | 123 | DI | PUFFMASTER3K | 3 | MODEL | Model Number | 45-JFI |
4 | 123 | DI | PUFFMASTER3K | 4 | SERIAL | Serial Number | 456789132-AXQ |
5 | 123 | DI | PUFFMASTER3K | 5 | FDAUDI | FDA Unique Device Identifier | 456789123xyz |
6 | 123 | DI | PUFFMASTER2023 | 1 | DEVTYPE | Device Type | SmokeMachine |
7 | 123 | DI | PUFFMASTER2023 | 2 | MANUF | Manufacturer | Acme Machines |
8 | 123 | DI | PUFFMASTER2023 | 3 | MODEL | Model Number | 62-PLC |
9 | 123 | DI | PUFFMASTER2023 | 4 | SERIAL | Serial Number | 215964564-NFS |
10 | 123 | DI | UsualCTCigarette | 1 | DEVTYPE | Device Type | Combustible Tobacco Cigarette |
11 | 123 | DI | UsualCTCigarette | 2 | MANUF | Manufacturer | Philip Morris International |
12 | 123 | DI | UsualCTCigarette | 3 | MODEL | Model Number | Marlboro Red |
13 | 123 | DI | UsualCTCigarette | 4 | SERIAL | Serial Number | 123456789 |
- Entity IDs are unique within the assay (and a study can have many assays)
- Replicates vs. Run
- need planned (ei.xpt) separate from the actual (gt.xpt)
- If tests run at the same time, they are replicates and are assigned the same RUNID
- If tests are run at separate times, they are runs and the RUNIDs are distinct
- Different runs would be expected to have different ENID and GTDTC values. In ei.xpt, these are distinguished by different RUNID values.
- Entities that are replicates of each other would be expected to
- have different ENID values
- be in the same trial set (SETCD values)
- have the same RUNID values
| Row | STUDYID | ASSAYID | DOMAIN | ENID (Entity ID) | SETCD (from TX) | RUNID | REPNUM (perm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 123 | MNvit | EI | 1-8-3 | A1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 123 | MNvit | EI | 2-8-3 | A1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 123 | MNvit | EI | 2-9-3 | A1 | 2 | 1 | |
| 123 | MNvit | EI | 3-7-1 | A2 | 1 | 1 | |
| 123 | MNvit | EI | 2-7-1 | A2 | 1 | 2 |
A1: 
A2: 
- Different runs would be expected to have different ENID and GTDTC values. In ei.xpt, these are distinguished by different RUNID values.
| Row | STUDYID | ASSAYID | DOMAIN | ENID | GTSEQ | GTTESTCD | GTTEST | GTCELLEV (cells evaluated) | GTORRES | GTORRESU | GTSTRESC | GTSTRESN | GTSTRESU | GTDTC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 1-8-3 | 1 | RICC | Relative Increase in Cell Count | 154 | 0 | % | 0 | 0 | % | 2022-05-25 |
| 2 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 1-8-3 | 2 | RCC | Relative Cell Count | 154 | 0 | % | 0 | 0 | % | 2022-05-25 |
| 3 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 1-8-3 | 3 | RPD | Relative Population Doubling | 154 | 0 | % | 0 | 0 | % | 2022-05-25 |
| 4 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 1-8-3 | 4 | MNCELLS | Micronucleated Cells | 2205 | 15 | Cells | 15 | 15 | Cells | 2022-05-25 |
| 5 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 1-8-3 | 5 | MNCELLS | Micronucleated Cells | 2474 | 13 | Cells | 13 | 13 | Cells | 2022-05-25 |
| 6 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 1-8-3 | 6 | MNCELLS | Micronucleated Cells | 2758 | 17 | Cells | 17 | 17 | Cells | 2022-05-25 |
| 7 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 1-8-3 | 7 | MNCELLS | Micronucleated Cells | 2669 | 12 | Cells | 12 | 12 | Cells | 2022-05-25 |
| 8 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 1-8-3 | 8 | AVGREL | Average Relative MN Frequency | 0.57 | % | 0.57 | 0.57 | % | 2022-05-25 | |
| 9 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 2-8-3 | 1 | RICC | Relative Increase in Cell Count | 134 | 15.7 | % | 15.7 | 15.7 | % | 2022-05-25 |
| 10 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 2-8-3 | 2 | RCC | Relative Cell Count | 134 | 13.0 | % | 13.0 | 13.0 | % | 2022-05-25 |
| 11 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 2-8-3 | 3 | RPD | Relative Population Doubling | 134 | 7.9 | % | 7.9 | 7.9 | % | 2022-05-25 |
| 12 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 2-8-3 | 4 | MNCELLS | Micronucleated Cells | 3266 | 20 | Cells | 20 | 20 | Cells | 2022-05-25 |
| 13 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 2-8-3 | 5 | MNCELLS | Micronucleated Cells | 2190 | 17 | Cells | 17 | 17 | Cells | 2022-05-25 |
| 14 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 2-8-3 | 6 | MNCELLS | Micronucleated Cells | 2758 | 13 | Cells | 13 | 13 | Cells | 2022-05-25 |
| 15 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 2-8-3 | 7 | MNCELLS | Micronucleated Cells | 2714 | 21 | Cells | 21 | 21 | Cells | 2022-05-25 |
| 16 | 123 | MNvit | GT | 2-8-3 | 8 | AVGREL | Average Relative MN Frequency | 0.66 | % | 0.66 | 0.66 | % | 2022-05-25 | |
| ... |
- No labels