Aneurysms in the aorta are classified based on their anatomical locations. Largely, they can be divided into two classes: thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA), those that are in the thoracic aorta, and abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), those that are in the abdominal aorta.
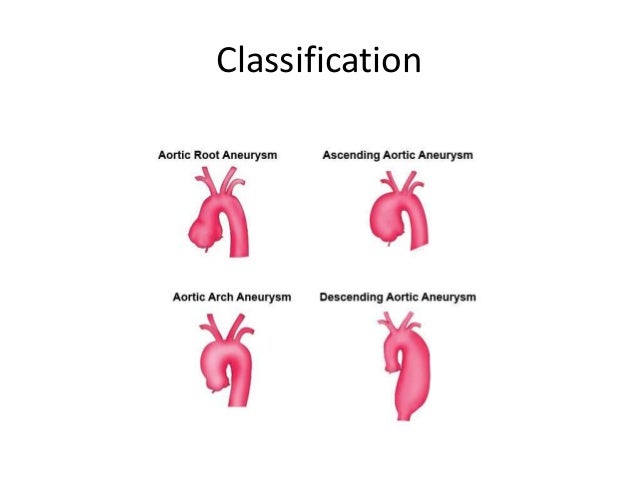 Image Added
Image Added
Thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) can further be divided into:
- Aortic root aneurysm
- Ascending aortic aneurysm
- Aortic arch aneurysm
- Descending aortic aneurysm
- Aneurysm that straddles multiple portions of the aorta (i.e. from aortic arch to descending aorta)
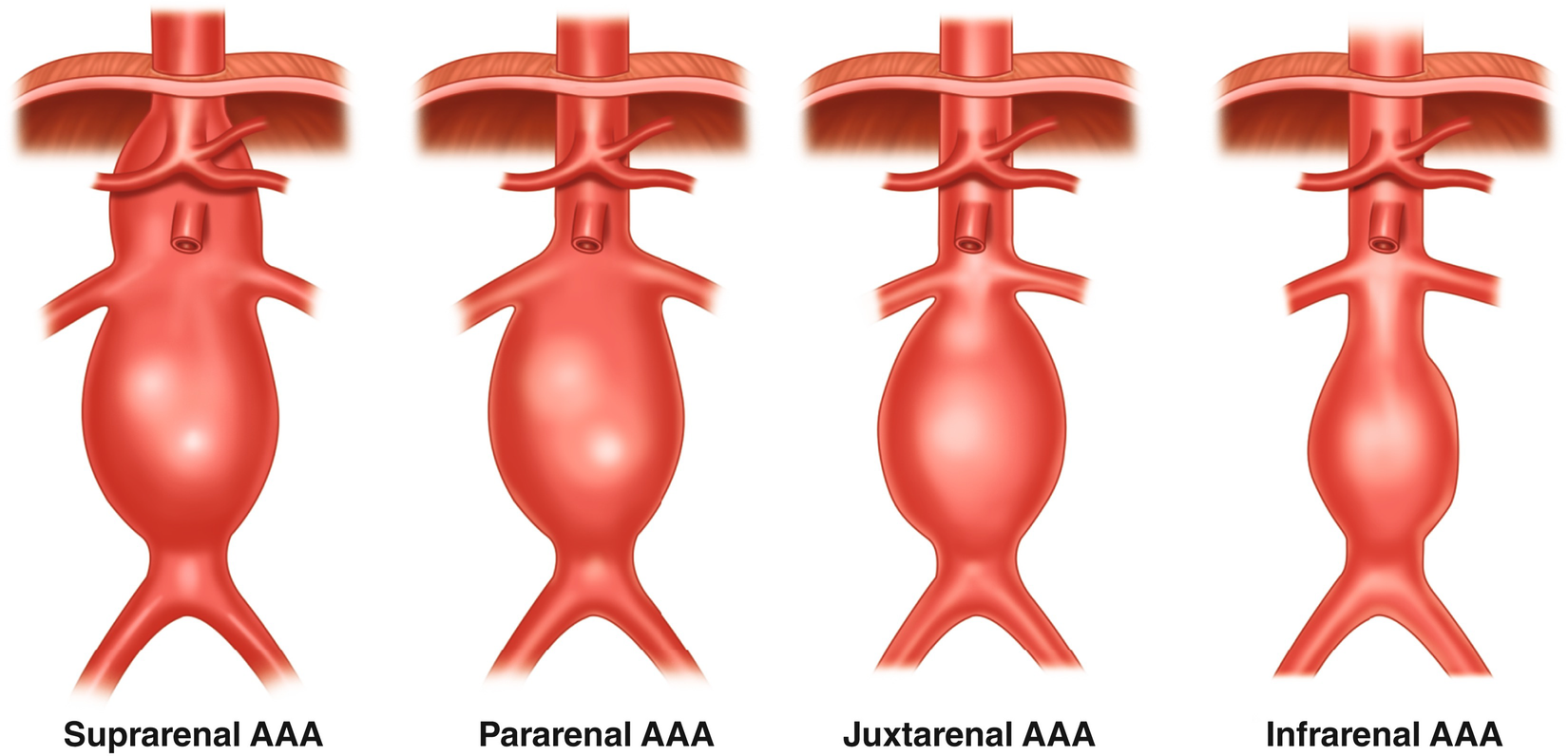 Image Added
Image Added
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) can be classified as:
- Suprarenal aortic aneurysm: above the kidneys
- Infrarenal aortic aneurysm: below the kidneys.
- Others: Pararenal, Jaxtarenal aortic aneurys.
Most patients with aortic aneurysms (AA) are asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis, because the aneurysms are typically discovered incidentally on imaging studies. When an AA reaches medium to large size (>5cm), symptoms may manifest.
The patient had undergone a diagnostic intervention, during which a CT scan was done on the chest and abdomen of the subject. The CT scan created images of the thoracic and abdominal regions. An evaluator then reviewed the images of the thoracic region and abdominal region, to find whether aneurysms and arterial dissections are present and where they are located.
| Excerpt Include |
|---|
| TAA and AAA concept map 2 |
|---|
| TAA and AAA concept map 2 |
|---|
|
Case 1 - Subject has both TAA and AAA
The subject had CT scans performed on the chest and abdomen.The subject had CT scans performed at the chest and abdomen to look for the presence of aneurysms, if there are any:
| Dataset wrap |
|---|
|
| Dataset2 |
|---|
Row | STUDYID | DOMAIN | USUBJID | PRSEQ | PRTRT | PRLOC | VISIT |
|---|
| 1 | ABC | PR | ABC-123 | 1 | CT SCAN | CHEST | BASELINE |
|---|
| 2 | ABC | PR | ABC-123 | 2 | CT SCAN | ABDOMEN | BASELINE |
|---|
|
|
If both AAA and TAA are found, and modeled as CE:
Note: in this case CE works because both TAA and AAA are detected so you would have separate CE record for each identified aneurysmAn evaluator examines the images of the thoracic and abdominal regions produced by the CT scan and decides whether TAA and AAA are present as well as their location. Modeling both TAA and AAA in the CV domain, note for viewing simplicity, some variables are omitted from the table below.
| Dataset wrap |
|---|
|
| Dataset wrap |
|---|
|
| Dataset2rowcaps |
|---|
STUDYID | DOMAIN | USUBJID | CESEQ | CETRT | CELOC | VISIT | CE LOC Detail | 1 | ABC | CE | ABC-123 | 1 | aneurysm | thoracic cavity | BASELINE | aortic root | 2 | ABC | CE | ABC-123 | 2 | aneurysm | thoracic cavity | BASELINE | Aortic arch to descending aorta | 3 | ABC | CE | ABC-123 | 3 | aneurysm | abdominal cavity | BASELINE | Infrarenal artery (Below the kidneys) | |
|
The FACE dataset would be the same as Richard's example.
If both AAA and TAA are found, and modeled as CV:
| 1: | I examined the image of the thoracic region (test location) and found an aneurysm in the Thoracic Aorta (result location) spanning from the aortic arch to the descending aorta (result location detail). In this case result location detail further qualifies both ORRES and RESLOC, hence this is a variable qualifier. |
|---|
| Row 2: | I measured the diameter of the aneurysm from aortic arch to the descending aorta (test location). |
|---|
| Row 3: | I examined the image of the thoracic region (test location) and found that the descending aorta (result location) had severely dissected (the artery is tore and a false lumen had formed), most likely due to the enormous pressure caused by the large aneurysm in this area. |
|---|
| Row 4: | The dissected descending aorta (test location) is classified based on the Stanford Aortic Dissection System as type B. |
|---|
| Row 5: | I examined the image of the abdominal region (test location) and found an aneurysm in the infrarenal aorta (result location), proximal to the iliac bifurcation (result location detail). In this case result location detail is a variable qualifier for the result, I am trying to say that the aneurysm is located in the segment of the infrarenal aorta closer (proximal) to the iliac bifurcation. |
|---|
| Row 6: | I measured the diameter of the infrarenal aortic (test location) aneurysm. |
|---|
| Row 7: | I examined the image of the abdominal region and found that the infrarenal aorta (result location) had dissected. |
|---|
|
|
| Dataset2 |
|---|
Row | STUDYID | DOMAIN | USUBJID | CVSEQ | CVGRPID | CVTEST | CVORRES |
|---|
CVORRESUCVLAT | CVLOCDTL | CVMETHOD | VISITNUM | VISIT | CVDTC |
|---|
CV RES LOC
| CV RES LAT | CV Result LOC detail | 1 | ABC | CV |
| CVRESLOC
| CVRESLOC Detail |
|---|
| 1 | ABC | CV | ABC |
|---|
ABC 1 Ythoracic cavity
| Thoracic region |
| CT SCAN | 1 | BASELINE |
2020 2 | ABC | CV | ABC-123 | 2 | 1 | Number of Aneurysms | 2 | | Aortic Arch to Descending aorta | | 2 | ABC | CV | ABC-123 | 2 | 1 | Aneurysm Diameter | 6 | cm | Thoracic Aorta | Aortic Arch to Descending aorta | CT SCAN | 1 | BASELINE | 2020-04-27 |
|
|
|
|---|
| 3 | ABC | CV | ABC-123 | 3 | 2 | Dissection Indicator | Y |
| Thoracic region |
|---|
thoracic cavity 2020Aorta 3 ABC CV ABC 3 | 4 | 2 | Stanford AoD Classification | Stanford B |
| Descending aorta |
| CT SCAN | 1 | BASELINE |
Aneurysm Length/Diameter | 2 | CM | | 2020-04-27 |
|
|
| | 5 | ABC | CV | ABC-123 | 5 | 3 | Aneurysm Indicator | Y |
| Abdominal region |
|---|
aorta 2020Aortic root | 3 | ABC | CV | |
| Infrarenal aorta | proximal to the iliac bifurcation | | 6 | ABC | CV | ABC |
|---|
ABC 41 Length/ 7.5 CM| cm | Infrarenal aorta | proximal to the iliac bifurcation | CT SCAN | 1 | BASELINE |
2020Aortic Arch to Descending Aorta | 4 | ABC | CV | ABC-456 | 1 | 2 | Aneurysm abdominal cavity
| Abdominal region |
| CT SCAN | 1 | BASELINE | 2020-04-27 |
RENAL ARTERY | LEFT | 5 | ABC | CV | ABC-456 | 2 | 2 | Aneurysm Length/Diameter | 3 | CM | renal artery | left | CT SCAN | 1 | BASELINE | 2020-04-27 | 6 | ABC | CV | ABC-456 | 3 | 3 | Aneurysm Indicator | Y | abdominal cavity | CT SCAN
| Infrarenal aorta | proximal to the iliac bifurcation |
|
|
Case 2 - Subject has AAA but TAA is not found
The subject had a MRI performed on the torso (trunk).
| Dataset wrap |
|---|
|
| Dataset2 |
|---|
Row | STUDYID | DOMAIN | USUBJID | PRSEQ | PRTRT | PRLOC | VISIT |
| PRLOC1 | PRLOC2 |
|---|
| 1 | ABC | PR | ABC-456 | 1 | MRI | Multiple | BASELINE |
| Chest | Abdomen |
|---|
|
|
The MRI scan produced images about the thoracic and abdominal regions of the subject. The evaluator then examined the MRI images of the thoracic region and abdominal region, and found the presence of a large AAA, but the absence of TAA.
| Dataset wrap |
|---|
|
| Rowcaps |
|---|
| Row 1: | I examined the MRI image of the thoracic region (test location) and didn't find the presence of an aneurysm. |
|---|
| Row 2: | I examined the MRI image of the abdominal region (test location) and found an aneurysm in the left (Result LAT) renal artery (Result Loc). |
|---|
| Row 3: | I examined the image of the abdominal region (test location) and found an aneurysm in the infrarenal aorta (Result Loc). |
|---|
| Row 4: | I measured the diameter of the aneurysm in the left renal artery (test location). |
|---|
| Row 5: | I measured the diameter of the aneurysm in the Infrarenal Aorta (test location). |
|---|
|
| Dataset2 |
|---|
Row | STUDYID | DOMAIN | USUBJID | CVSEQ | CVGRPID | CVTEST | CVORRES | CVORRESU | CVLOC | CVLAT | CVMETHOD | VISITNUM | VISIT | CVDTC |
| CVRESLOC
| CVRESLAT |
|---|
| 1 | ABC | CV | ABC-456 | 1 |
| Aneurysm Indicator | N |
| Thoracic Region |
| MRI | 1 | BASELINE | 2020-04-27 |
|
|
|
|---|
| 2 | ABC | CV | ABC-456 | 2 | 1 | Aneurysm Indicator | Y |
| Abdominal Region |
| MRI | 1 | BASELINE | 2020-04-27 |
| Renal Artery | Left |
|---|
| 3 | ABC | CV | ABC-456 | 3 | 2 | Aneurysm Indicator | Y |
| Abdominal Region |
| MRI | 1 | BASELINE | 2020-04-27 |
| Infrarenal |
|---|
artery (Below the kidneys)7 | ABC | CV | ABC 43 Length/Diameter2 | CM | abdominal cavity | Infrarenal artery (Below the kidneys) | CT SCAN| Diameter | 3 | cm | Renal Artery | Left | MRI | 1 | BASELINE | 2020-04-27 |
|
|
| | 5 | ABC | CV | ABC-456 | 5 | 2 | Aneurysm Diameter | 5 | cm | Infrarenal Aorta |
| MRI | 1 | BASELINE |
|---|
2020
|
|

