move assumptions out of all of the examples
add row captions to highlight exceptions/assumptions
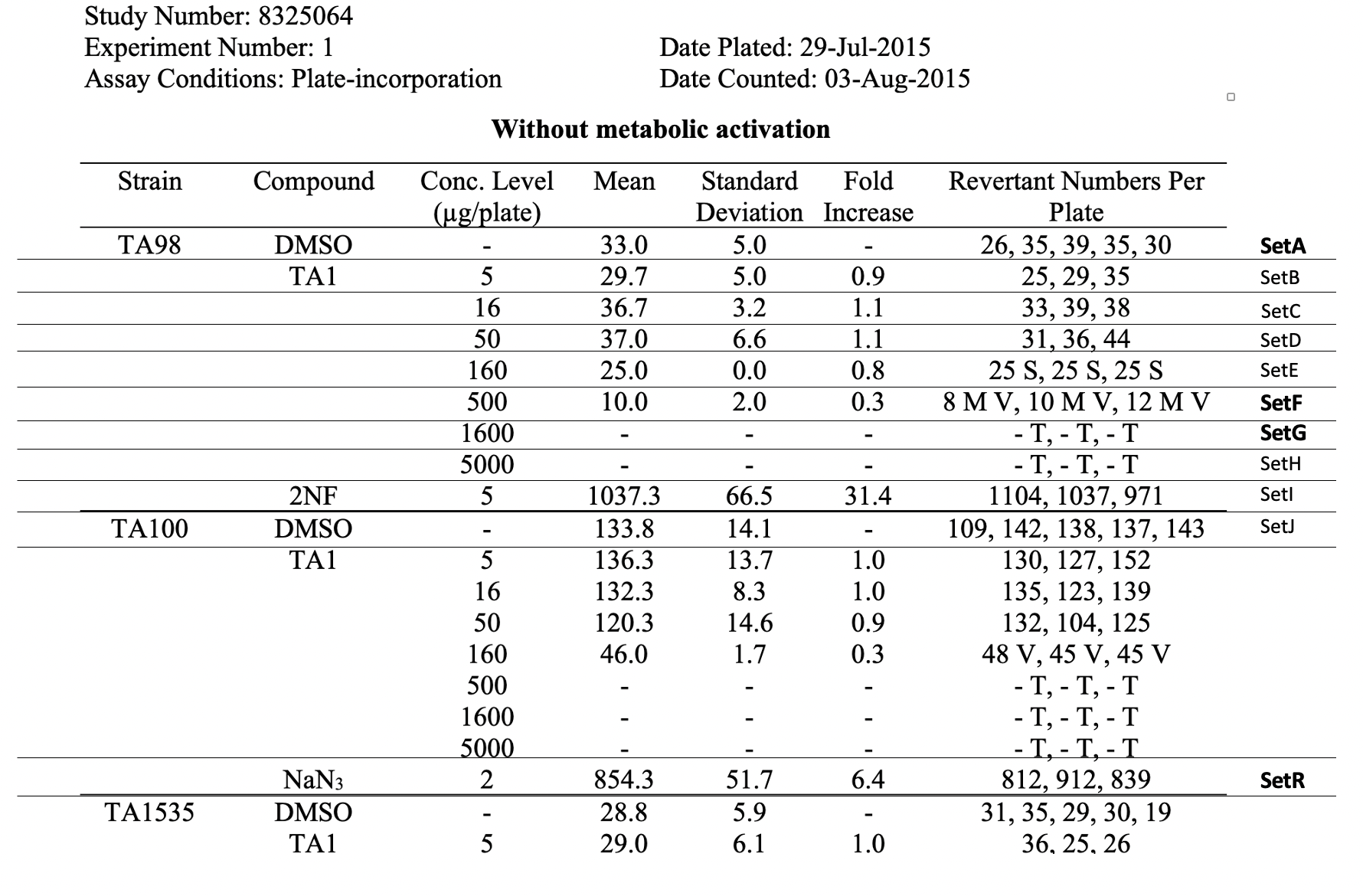
This is an example showing trial design and results from the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation test of Study #8325064. The bacterial reverse mutation test uses four different amino acid-requiring strains of Salmonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium) and one strain of Escherichia coli (E. coli) to detect point mutations, which involve substitution, addition or deletion of one or a few DNA base pairs. The principle of this bacterial reverse mutation test is that it detects
- How do we handle "toxic, no revertant colonies"? (LAK will add 6 records with GTSTAT = NOT DONE, GTREASND = "TOO MUCH CYTOTOXICITY,"
- When "-" in Mean, Std Dev, Fold Inc - refer to SEND team's marked-up table (GTSTAT = NOT DONE; variety of REASND)
- recreate the data table - clean up, add "S" to the first set A
- move assumptions out of all of the examples
- add row captions to highlight exceptions/assumptions
This is an example showing trial design and results from the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation test of Study #8325064. The bacterial reverse mutation test uses four different amino acid-requiring strains of Salmonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium) and one strain of Escherichia coli (E. coli) to detect point mutations, which involve substitution, addition or deletion of one or a few DNA base pairs. The principle of this bacterial reverse mutation test is that it detects chemicals that induce mutations which revert mutations present in the S typhimurium and E. coli tester strains and restore the functional capability of the bacteria to synthesize an essential amino acid. The revertant bacteria are detected by their ability to grow in the absence of the amino acid required by the parent tester strain.
 Image Removed
Image Removed
. coli tester strains and restore the functional capability of the bacteria to synthesize an essential amino acid. The revertant bacteria are detected by their ability to grow in the absence of the amino acid required by the parent tester strain.
 Image Added
Image Added
Assumption: When the experimental unit is derived from the species and strain, such as a cell line, then TESTSYS should be supplied.
In this example, the Trial Summary dataset, ts.xpt, includes many informational fields that may provide context at the study level, for Study 8325064. Also, TSGRPID has been used to link records (name, location, country) related to the test facility (TSGRPID = 1) and records related to the Test Site (TSGRPID = 2). The Study Director is associated with the Test Facility and the Principal Investigator is associated with the Test Site. Finally, the Primary Treatment CAS Registry Number is not known and this is recorded as an empty TSVAL and UNKNOWN in the corresponding TSVALNF.
| Dataset wrap |
|---|
| Rowcaps |
|---|
| Rows 1-2: | Shows two records for TSPARMCD = "GLPTYP", using TSSEQ to indicate multiple records, since both GLP Types apply for this example study. | | Rows 9-12: | TSGRPID has been used to link records (name, location, country) related to the test facility (TSGRPID = 1). The Study Director is associated with the Test Facility. | | Rows 18-24: | Shows that this example study includes two different species of bacteria and a total of five strains. | | Rows 18-22: | Shows that TSGRPID (TSGRPID = 2) has been used to link the information for one species (Salmonella) with four different strains that are tested in this example study. | | Row 23-24: | Shows that TSGRPID (TSGRPID = 3) has been used to link the information for one species (Escherichia coli) with the strain that is tested in this example study. |
|
|
| Expand |
|---|
| title | ts.xpt (trial summary, study level parameters) |
|---|
|
Assumption: When the experimental unit is derived from the species and strain, such as a cell line, then TESTSYS should be supplied. |
|---|
Row | STUDYID | ASSAYID | DOMAIN | TSSEQ | TSGRPID | TSPARMCD | TSPARM | TSVAL | TSVALNF |
|---|
1 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 |
| GLPTYP | Good Laboratory Practice Type | FDA |
|
|---|
2 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 2 |
| GLPTYP | Good Laboratory Practice Type | OECD |
|
|---|
3 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 |
| STSTDTC | Study Start Date | 2015-07-29 |
|
|---|
4 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 |
| STITLE | Study Title | The Bacterial Reverse Mutation Test, Study 8325064-1 |
|
|---|
5 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 |
| SNDIGVER | SEND Implementation Guide Version | TOBACCO IMPLEMENTATION GUIDE VERSION 1.0 |
|
|---|
6 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 |
| SNDCTVER | SEND Controlled Terminology Version | SEND Terminology 2021-09-30 |
|
|---|
7 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 |
| SSPONSOR | Sponsor Organization | Example Sponsor Inc. |
|
|---|
8 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 |
| SPREFID | Sponsor's Study Reference ID |
| NOT APPLICABLE |
|---|
9 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 | 1 | TSTFNAM | Test Facility Name | Example Tox Lab Name |
|
|---|
10 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 | 1 | TSTFLOC | Test Facility Location | 10 Somewhere Street, Montgomery, AL 10000 |
|
|---|
11 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 | 1 | TFCNTRY | Test Facility Country | USA |
|
|---|
12 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 | 1 | STDIR | Study Director | Dr. R. Smith |
|
|---|
13 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 |
| GLPFL | GLP Flag | N |
|
|---|
14 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 |
| ASTD | Assay Standard | OECD Test No. 471 |
|
|---|
15 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 |
| ASTDV | Assay Standard Version | 2020-06-29 |
|
|---|
16 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 |
| SSTYP | Study Type | GENOTOXICITY IN VITRO |
|
|---|
17 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 |
| SSSTYP | Study Sub Type | Bacterial Reverse Mutation Test |
|
|---|
18 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 | 2 | SPECIES | Species | Salmonella |
|
|---|
19 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 | 2 | STRAIN | Strain | TA98 |
|
|---|
20 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 | 2 | STRAIN | Strain | TA100 |
|
|---|
21 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 | 2 | STRAIN | Strain | TA1535 |
|
|---|
22 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 | 2 | STRAIN | Strain | TA1537 |
|
|---|
23 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 | 3 | SPECIES | Species | Escherichia coli |
|
|---|
24 | 8325064 | Ames | TS | 1 | 3 | STRAIN | Strain | WP2 uvrA pKM101 |
|
|---|
|
|
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Raw Data Table for Study 8325064 |
|---|
|
|
...


