Page History
Aortic Aneurysms in the aorta are classified based on their anatomical locations. Largely, they can be divided into two classes: thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA), those that are in the thoracic aorta, and abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), those that are in the abdominal aorta.
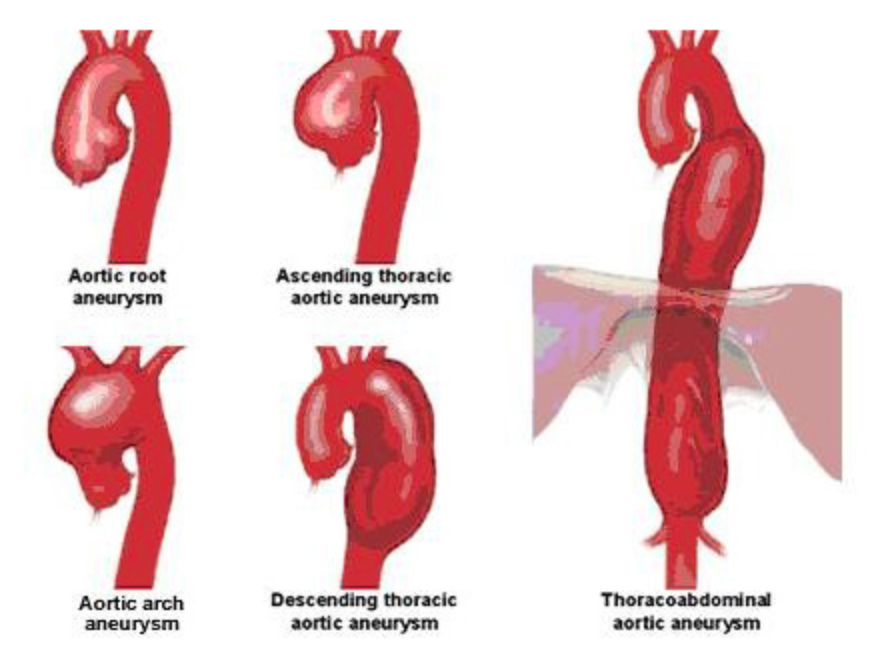
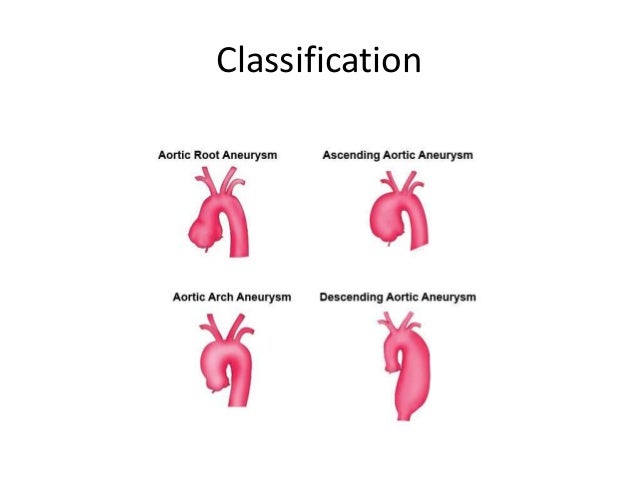
Thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) can further be divided into:
- Aortic root aneurysm
- Ascending aortic aneurysm
- Aortic arch aneurysm
- Descending aortic aneurysm
- Aneurysm that straddles multiple portions of the aorta (i.e. from aortic arch to descending aorta)
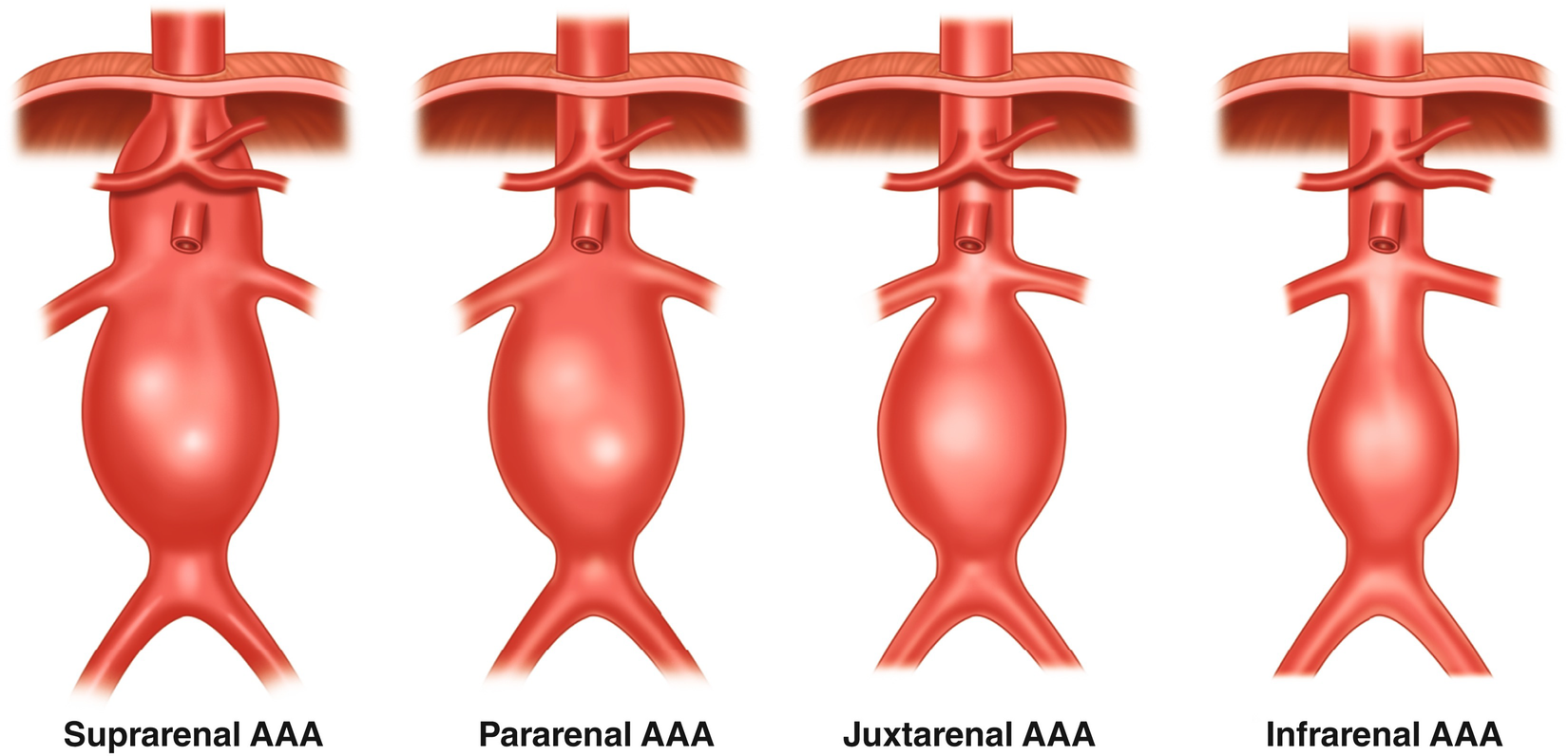
AAA can Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) can be classified as:
- Suprarenal aortic aneurysm: above the kidneys
- Infrarenal aortic aneurysm: below the kidneys.
- Others: Pararenal, Jaxtarenal aortic aneurys.
...
When a patient has abdominal aortic aneurysm of a substantial size, the patient may also have synchronous and metachronous thoracic aortic aneurysm. If causes and conditions are present to create an aneurysm in a large-medium size vessel in one place, you are more likely than those without those causes and conditions to have (or develop) another aneurysm somewhere. The pressure from the medium to large aneurysm may also cause arterial dissection where the wall of the artery is tore, and a "false lumen" forms within the wall of the artery and blood can leak into it - leading to rupture.
...
The figure below describes the general process flow from when a patient complains about the symptoms indicative of TAA and AAA to the diagnosis of TAA and AAA, followed by their subsequent evaluationevaluations. This is a summary of all the data collected.
...
The concept map below transforms the general process figure above into CDISC-compliant format. Note the (TST) and (RES) prefixes are done intentional in the map below are used to show: test location and vs result location, respectively.
...
The subject had a MRI performed on the upper body:.
| Dataset wrap | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
The evaluator then examined the MRI images of the thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity, and found the presence of a large AAA, but the absence of TAA.
| Dataset wrap | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
...